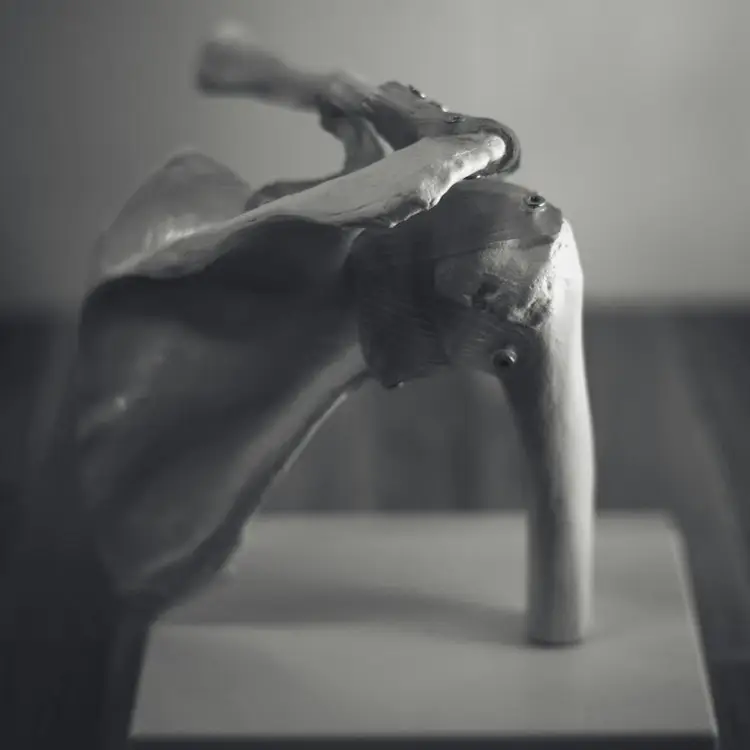
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and facilitating movement. Rotator cuff tears are a common source of shoulder pain and disability, particularly among athletes and individuals engaged in repetitive overhead activities. In this blog post, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for rotator cuff tears.
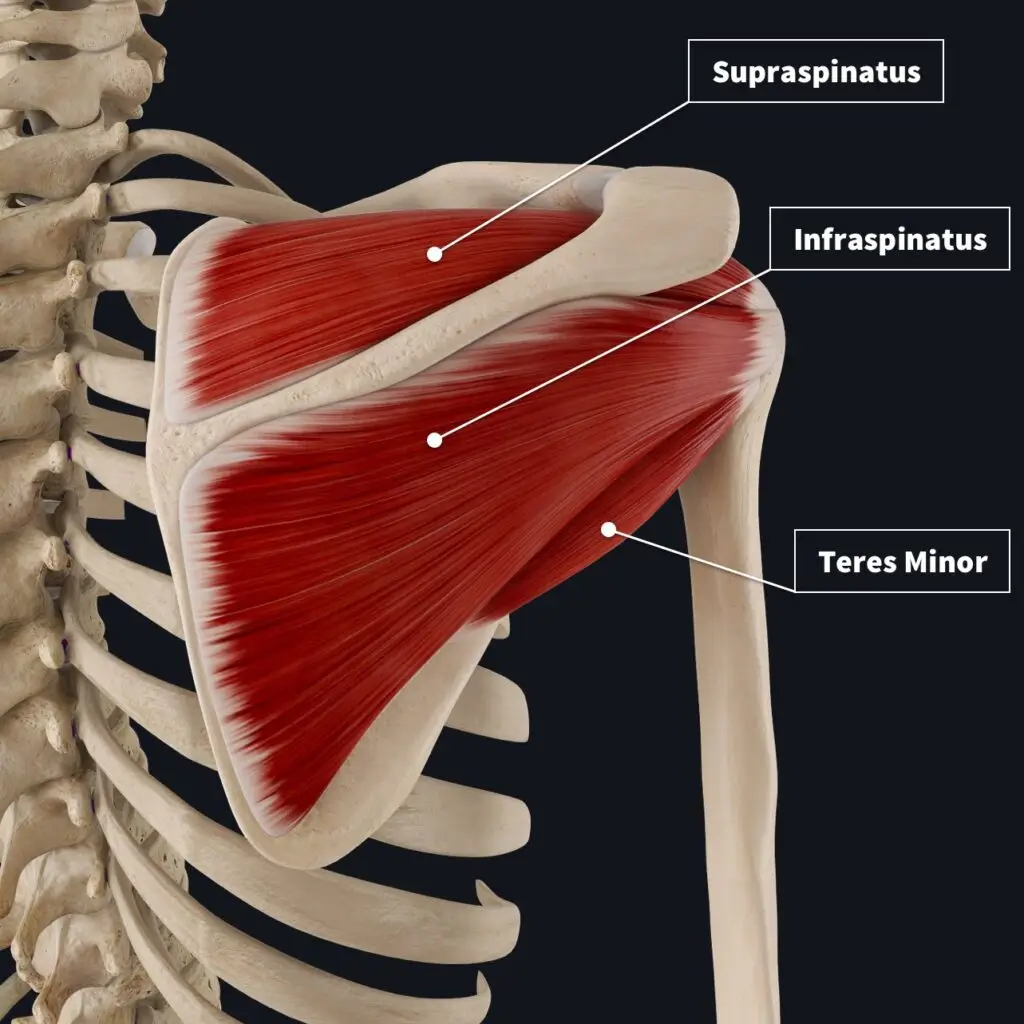

The most common causes of rotator cuff tears include:
- Traumatic Injury: Rotator cuff tears can occur from a fall onto an outstretched arm, a direct blow to the shoulder, or a sudden forceful movement.
- Degenerative Changes: As we age, the tendons of the rotator cuff can degenerate and weaken, making them more prone to tearing, especially with repetitive overhead activities.
- Overuse: Activities such as lifting heavy objects, repetitive throwing, or overhead sports like baseball and tennis can place excessive stress on the rotator cuff tendons, leading to tears over time.
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Tears:
The symptoms of a rotator cuff tear can vary depending on the severity of the tear, but common signs include:
- Shoulder pain, especially when lifting or lowering the arm.
- Weakness in the shoulder, particularly when attempting to lift or rotate the arm.
- Difficulty performing overhead activities or reaching behind the back.
- Crepitus or a crackling sensation in the shoulder joint. 5. Limited range of motion in the shoulder.
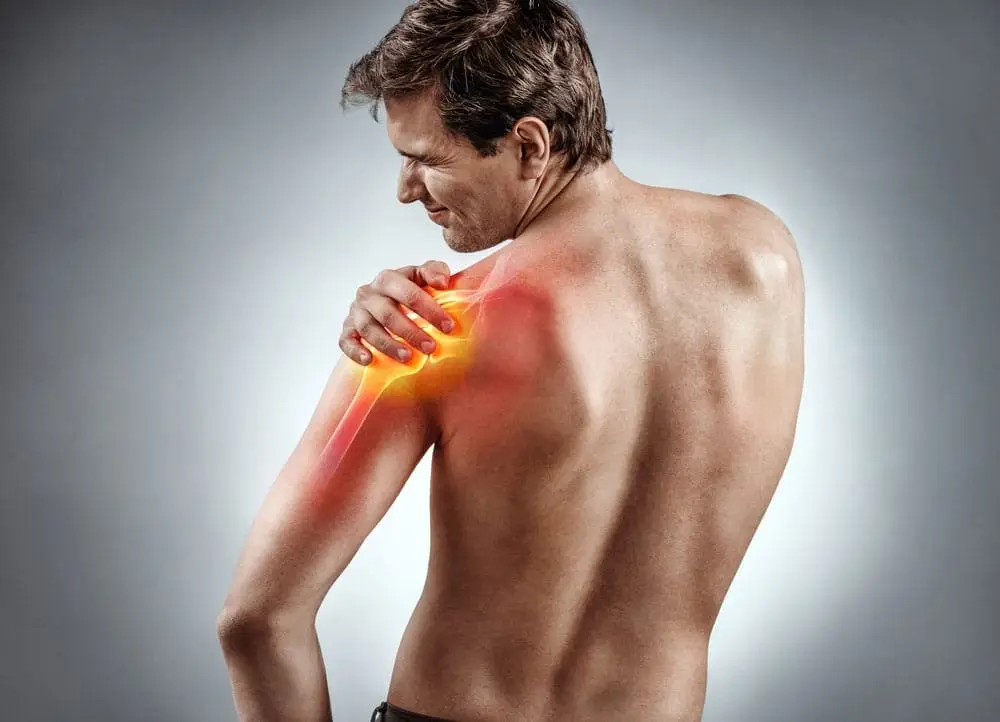

Diagnosis:
To diagnose a rotator cuff tear, a healthcare provider will typically perform a thorough physical examination, assess the patient’s medical history, and may order imaging tests such as an MRI or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the tear.
Treatment Options:
The treatment approach for rotator cuff tears depends on various factors, including the size and severity of the tear, the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Conservative Management: For small, partial tears or tears in patients who are not surgical candidates, conservative treatments such as rest, activity modification, physiotherapy, and anti-inflammatory medications may be recommended to alleviate pain and improve shoulder function.
- Surgical Intervention: For large, full-thickness tears or tears that fail to improve with conservative measures, surgical repair may be necessary. Surgery aims to reattach the torn tendon to the bone and may involve arthroscopic or open techniques, depending on the specific characteristics of the tear.
Rehabilitation:
Regardless of the chosen treatment approach, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process for rotator cuff tears. Physiotherapy exercises focused on strengthening the rotator cuff muscles, improving shoulder flexibility, and restoring normal movement patterns are essential for optimizing outcomes and preventing recurrent injury.
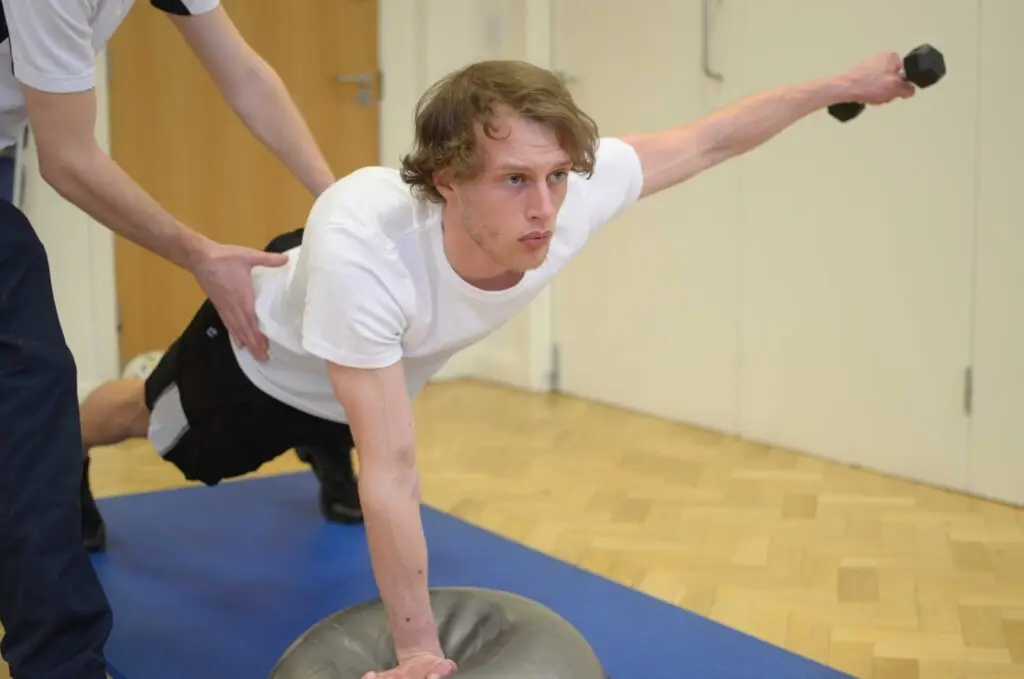


Rotator cuff tears can significantly impact shoulder function and quality of life, but with prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many individuals can experience significant improvement in symptoms and return to their desired level of activity. If you suspect you may have a rotator cuff tear or are experiencing persistent shoulder pain, consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Remember, early intervention is key to successful recovery and long-term shoulder health.